Sustainability and Traceability in the Food Industry: A Recipe for Responsible Consumption
The article emphasizes sustainability and traceability in the food industry, addressing the challenge of global demand while minimizing environmental impact. It highlights eco-friendly practices, traceability for transparency, and the role of technology, particularly blockchain.

The modern food industry faces an entirely new challenge: meeting the growing global demand for food while at the same time minimizing its environmental impact on society around us. With global concerns about climate change, resource depletion particularly in the third world, and ethical sourcing continue to gain momentum in the public eye - the concepts of sustainability and traceability have become crucial pillars for a responsible and accountable supply chain within the food industry.
Sustainability in the food industry goes beyond simply producing food. It includes a commitment to practices and processes, which preserve the environment, support local communities, and ensure the healthy planet and the well-being of both current and future generations. Sustainable agriculture focuses on minimizing the use of damaging chemicals, reducing water usage and waste as well as promoting biodiversity.

One key aspect of sustainability within agriculture is the reduction of the carbon footprint associated with food production. The food industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, from the cultivation of crops and animal farming to the transportation of goods and finished products. Sustainable practices and processes aim to reduce and eliminate these emissions through energy-efficient technologies, responsible land use, and eco-friendly packaging.
The Role of Traceability in Ensuring Accountability
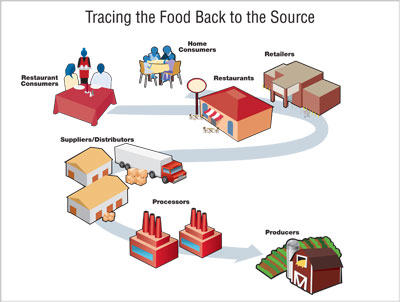
Traceability plays a crucial role in the aspect of the modern food industry. Traceability is the ability to track and trace all movements within the supply chain for food products and their ingredients from farm to counter. This transparency in the supply chain is essential for end-consumer health and safety, consumer verification of brand claims and for fostering loyalty accountability within the industry.
Traceability helps identify the origin of food products, providing consumers with information about where their food comes from, how it was produced, and the journey it took to reach their plate. This level of transparency enables consumers to make informed choices when purchasing food items, which are fully aligned with their values, regardless is those values are centred on environmental conscience, ethical sourcing believes or supporting local economies.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
A part of the foundation for sustainability within the food industry is the adoption of eco-friendly agricultural practices and processes. Traditional farming methods often rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, contributing to soil degradation and water pollution. Sustainable agriculture promotes organic farming, crop rotation, and agroforestry to enhance soil health and promote biodiversity.
Additionally, sustainable agriculture aims to reduce water usage through innovative irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting. Water scarcity is an increasing global concern, and the food industry must take a leading role in responsible water management to ensure a sustainable future for our society.
Reducing Food Waste
Another significant challenge the food industry faces is the staggering amount of food that goes to waste. In the various processes from farm to table, a substantial amount of food is lost due to inefficient harvesting, issues on transportation, and inadequate storage practices, as well as consumer behaviour. Food waste is a big problem globally. The western world has long had the unfortunate privilege of leading the world in food waste, but other emerging markets are sadly catching up. If brands adopt sustainable practices within their food supply chain, and focus more on marketing these efforts, then the consumers will gain greater awareness of the issues we are facing, including minimizing food waste at every possible stage.
By implementing technology that can help to share the story behind their products, brands can gain a competitive advantage and set themselves apart from the competition.
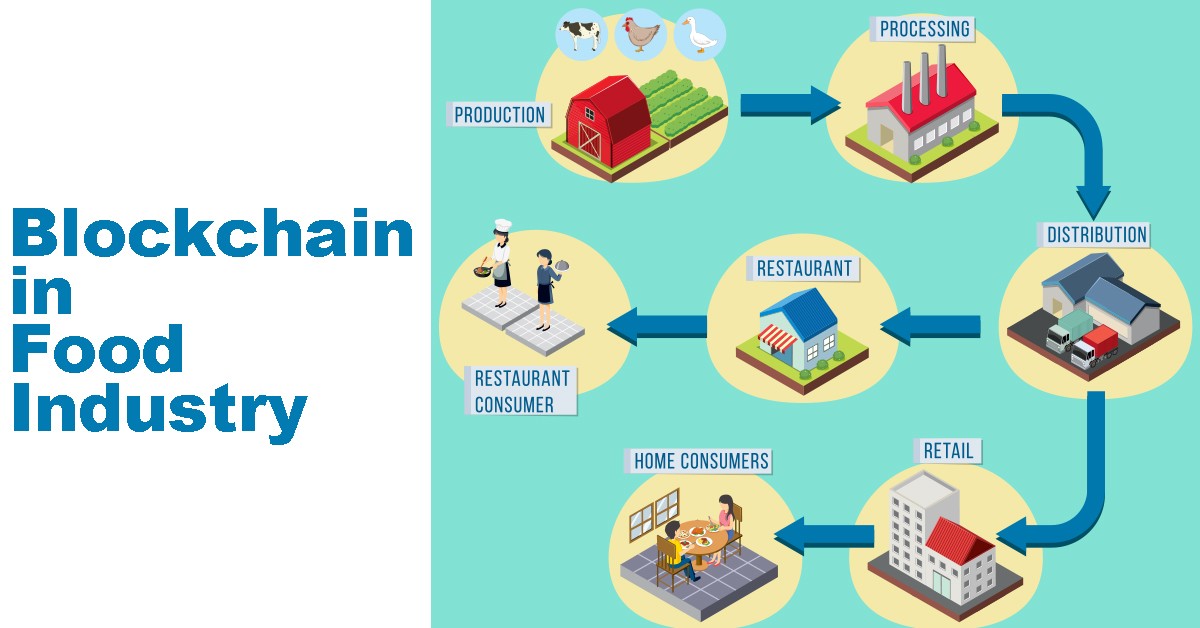
One option to achieve this could be the implementation of blockchain technology. Through blockchain technology brands can record each step of their process on an immutable ledger, which will allow the consuming public to verify the claims of sustainability and traceability set forth by the brand. This will help to build a stronger bond with the end-consumers, and promote these brands when consumers have to vote with their wallets in the supermarkets, the restaurants and during online purchases.
Other innovations within packaging, storage, and distribution technologies can help extend the shelf life of products presented to the consumers, reducing the likelihood of spoilage and waste. Additionally, initiatives to redirect surplus food to charities and food banks contribute to both social responsibility and waste reduction. Many companies help by donating to local foodbanks, churches or charities in an effort to make a difference in the local societies.
The Importance of Ethical Sourcing
Sustainability in the food industry extends beyond environmental considerations, and include social and ethical concerns as well. Ethical sourcing involves ensuring fair labour practices, humane treatment of animals, and support for local communities. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the ethical implications of their food choices, and companies are responding by adopting transparent and responsible sourcing practices.
Certification programs like Fair Trade, provide consumers with assurance that the products they purchase meet specific ethical standards. These certifications not only benefit farmers and workers but also empower consumers to use their purchasing power to drive positive change in the industry.
Implementing technologies with verifiable audit trails such as blockchain, will help to add additional credibility to global and regional certification programs. Overall blockchain can plat a very important role in promoting ethical sourcing within the food industry, by enhancing transparency, traceability, and accountability.
Consumer Empowerment through Information
Empowering consumers to make sustainable choices requires providing them with the necessary information to drive their decision making. From QR codes on product packaging that link to detailed supply chain information to mobile apps that offer insights into the environmental and social impact of various products, the food industry is leveraging technology to create a more informed and conscientious consumer base.

Educating consumers about the consequences of their food choices and offering alternatives that align with their values can drive demand for sustainable products. As consumers demand more sustainability and transparency, companies are incentivized to invest in sustainable practices and technology to maintain their market share.
Technology
In the quest for sustainability and traceability, technology plays a pivotal role. Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing the transparency and security of supply chains. By recording every transaction and movement of products on a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain ensures that information is fraud-proof and easily accessible.
This technology is particularly valuable in verifying the authenticity of organic and fair-trade labels, combating food fraud, and providing real-time information about the status of products in the supply chain. As consumers become more tech-savvy, the integration of blockchain and other technological solutions becomes not just a competitive advantage for companies but a necessity for meeting consumer expectations.
Challenges and Opportunities
While progress has been made in integrating sustainability and traceability into the food industry, challenges still exist for the industry. The transition to sustainable practices and processes can be costly, requiring investments in new technologies, additional training for farmers, and changes in established supply chain processes. On top of all this, the complexity of global supply chains within the food industry, presents challenges in ensuring traceability especially for products with numerous ingredients sourced from different regions.
These challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. Governments, businesses, and end-consumers all have a role to play in driving positive change within the industry. Incentives for sustainable practices, supportive policies, and consumer education campaigns can collectively contribute to a more sustainable and transparent food industry.

Conclusion
The intersection of sustainability and traceability is reshaping the food industry, challenging traditional practices, and inspiring a new era of responsible production and consumption from the consumers. As consumers become increasingly conscious of the environmental and social impact of their food choices, the industry must respond with sustainable and traceable solutions.
From embracing eco-friendly agricultural practices to leveraging technology for transparent supply chains, the path to a sustainable food future is multifaceted. The collaboration of stakeholders, from farmers to consumers, is essential for building a resilient and responsible food supply chain that nourishes both people and the planet.
In this evolving landscape, the food industry has the opportunity to not only meet the demands of the present but also to cultivate a legacy of sustainability for generations to come. Through sustainable practices, innovative technologies and transparent supply chains, the food industry can redefine its role in shaping a healthier, more equitable, and environmentally conscious world.
