A circular approach: Revolutionizing recycling frameworks in corporate practices with blockchain technology
Companies are shifting to a circular economy, prioritizing sustainability through durable product design and innovative models like leasing. Advanced recycling tech and blockchain enhance transparency, positioning businesses as leaders in responsible resource management.
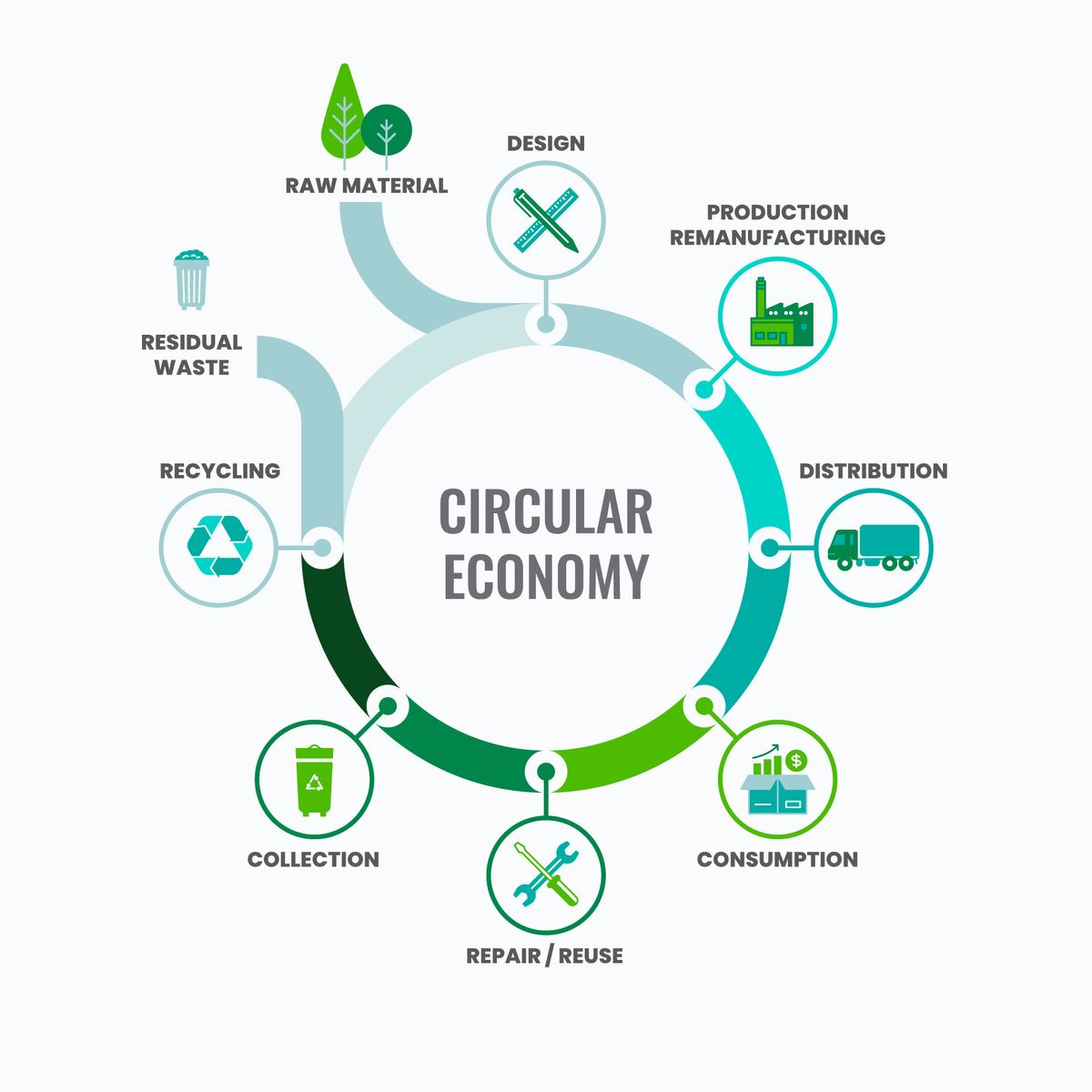
In a time where we are faced with unprecedented environmental challenges and a growing global conscience among consumers when it comes to sustainability, many companies are increasingly recognizing the importance of implementing a circular framework approach to recycling into their corporate practices, to reduce the overall environmental impact of their on-going operations.
The traditional business models in a ‘create, use & dispose’ society is not meeting the sustainability requirements of our modern society, and leads to resource depletion in parts of the world, which are already struggling with climate change driven changes in their local environments.
Here we will explore the recycling frameworks in the world of business today, with a specific focus on the circular economy, a concept that prioritizes reducing, reusing, and recycling materials to create a regenerative system, that decreases the need for virgin raw materials in on-going productions.

The circular framework seeks to close the loop by keeping products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible. This will ensure a sustainable and regenerative system. This shift is not only environmentally beneficial but also economically advantageous for businesses that embrace it, fostering a more sustainable and resilient global economy. Reducing the need for new fresh resources will bring increased economic benefits for companies, once they have invested in facilities or partnerships that will allow for extracting materials from recycled products.
Key principles of the circular framework
Companies are increasingly focusing on designing products with longevity in mind, ensuring durability while making products easier to repair. By creating products that can be taken apart with ease and repaired or upgraded, companies contribute to the extension of the product life cycle, reducing the need for constant replacements and minimizing the environmental impact associated with frequent product turnover. Upgrading internal hardware on electronics will make it possible to extend the lifecycle of the most rapidly evolving product segment.
Circular frameworks emphasize the importance of using materials that can be easily recycled or repurposed. Companies are adopting materials that have a lower environmental impact and can be reintroduced into the production cycle, thus minimizing waste and resource depletion. Investments into sustainable materials and advanced uses of the available resources is high on the list of companies, who are focusing on a circular framework as a backbone of their business.

Some industries are looking at shifting pivotal parts of their business, in order to achieve a sustainable foundation, from where they can implement circular frameworks for sustainability. Leasing their products instead of selling them to consumers, means that companies maintain ownership of their products, and keep the spent material resources within their own eco-system, ensuring proper maintenance throughout the lifecycle of the products, and complete access to their products for the recycling processes when their products reach the end-of-life stage.
Instead of disposing of waste, a circular framework solution emphasizes the concept of upcycling, where waste materials are transformed into new, high-quality products. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact but also brings innovation in finding creative ways to repurpose materials, driving the development of a circular innovation ecosystem.
Implementing Circular Frameworks in Corporate Recycling
Companies are integrating circular principles into their supply chains, as they chase sustainability as a corporate goal, by collaborating with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. From sourcing sustainable raw materials to implementing renewable energy manufacturing processes, a circular supply chain ensures that environmental impact is minimized at every stage. This integration involves implementing circular principles, as well as encouraging a unified commitment to sustainability throughout the entire supply network – both upstream and downstream.
To enhance the effectiveness of circular framework within their operations, companies are investing in efficient reverse logistics systems. This concept revolves around the collection and return of used products for repair, upgrading, or recycling. By establishing effective reverse logistics processes, companies can close the loop on their products and material resources, reducing waste and environmental impact while simultaneously creating opportunities for jobs being created in the local community, as well as improving the skills, experience and offerings of the local and regional recycling sector.

Many companies are investing in state-of-the-art recycling technologies, to lead the charge on circular framework implementation by embracing technological advancements. From advanced sorting systems to chemical processes that break down complex materials, these innovations enable more materials to be recycled and reused, pushing the boundaries of what was previously considered impossible. Continued research and development in recycling technologies is essential, to unlocking new possibilities and addressing the challenges connected to supply chains with diverse material flows.
Many governments are implementing Extended Producer Responsibilities (EPR) policies, through which they can hold companies accountable for the entire life cycle of their products. This encourages businesses to design products with recycling in mind and to take an active role in the management and recycling of their products after use. EPR’s do not only shift the majority of the responsibility on manufacturers, it also encourages collaboration between governments, businesses, and consumers in creating a sustainable and circular economy.
The integration of blockchain technology is emerging as a game-changer in the pursuit of a circular economy. Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability across the entire supply chain, through the inherent immutability and secure ledger systems within the blockchain’s underlying technology. By recording every step of a product's journey on an immutable blockchain, companies can ensure that materials are responsibly sourced, produced according to leading sustainably standards, and end-of-life recycling or upcycling is accurately documented. This allows suppliers to start offering rebates to their downstream customers at the time of sale, based on the recycling and reuse of materials, providing a strong financial incentive to implement state-of-the-art recycling and upcycling programs, based on the overall circular framework.
Blockchain facilitates the creation of a transparent and tamper-resistant ledger of a product's life cycle, providing consumers with unprecedented visibility into the sustainability practices of the products they choose to purchase. This transparency builds on trust, and empowers consumers to make informed choices that align with their values. This incentivizes businesses to adopt and maintain circular practices, and sharing highly relevant information about these processes, with their downstream consumers.

Additionally, blockchain can streamline the complex logistics of reverse supply chains. Smart contracts can automate and optimize the return, refurbishment, and recycling processes within a corporate supply chain. This not only reduces operational costs, but also have the ability to ensure that products reach their end-of-life destinations efficiently, contributing to the overall effectiveness of circular frameworks.
Conclusion
As the global community struggles with the multiple challenges inflicted on our society by climate change, depletion of resources, and environmental impacts all across the globe, the broad implementation and adoption of circular frameworks in corporate recycling practices becomes increasingly important, if we want to ensure a viable future for our children’s children. Companies that implement the circular frameworks into their operations not only contribute to environmental sustainability, they also position themselves as leaders in innovation and sustainable business practices. The integration of blockchain technology adds a layer of transparency and efficiency to these efforts, ensuring that circular framework practices are not only adopted by the corporations, but also verifiable, accountable and shareable with the downstream consumers and general public.
The transition to a circular framework practices requires a holistic approach to managing a business, involving collaboration across industries, advancements through technology, and a fundamental shift in mindset of upper corporate management across industries. The journey towards a circular framework in corporate recycling is undoubtedly challenging, but the long-term benefits for the environment, society, and the economy make it a journey worth committing to. As we strive for a more sustainable and regenerative future together as a society, the circular frameworks combined with blockchain technology, stands as a beacon of hope for all of us, guiding businesses toward sustainable practices that align with the principles of responsible resource management and environmental stewardship globally.
