Nurturing Sustainability and Traceability in the Copper Industry: A Path to Responsible Resource Management
Explore how the copper industry is innovating sustainability and traceability to tackle environmental challenges.

The copper industry stands at a pivotal junction where the imperatives of sustainability and traceability intersect with its operations. As one of the most widely used metals globally, copper holds indispensable importance in various sectors, including construction, electronics and transportation.
However, the extraction and processing of copper present significant environmental and social challenges. To navigate these complexities, the industry is increasingly embracing sustainable practices and enhancing traceability throughout the supply chain. This article explores the evolving landscape of sustainability and traceability in the copper industry, highlighting key initiatives, challenges and opportunities for fostering responsible resource management.

Sustainability in the copper industry encompasses a multifaceted approach that addresses environmental, social and economic dimensions. At its core, sustainable copper production seeks to minimize adverse environmental impacts, promote community well-being and ensure long-term viability. Key aspects of sustainable practices include:
Environmental Stewardship: The mining and processing of copper can result in habitat destruction, water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable initiatives aim to mitigate these impacts through measures such as efficient water and energy use, waste minimization and reclamation of mining sites. Advanced technologies, such as automated monitoring systems and innovative water treatment methods, are increasingly being deployed to reduce environmental footprints.

Social Responsibility: Copper mining often occurs in regions with indigenous communities and vulnerable populations. Sustainable practices prioritize meaningful engagement with local stakeholders, respect for human rights and equitable distribution of benefits. Community development programs, such as education and healthcare initiatives, contribute to enhancing social well-being and fostering positive relationships between mining companies and host communities.
Economic Resilience: Sustainable copper production entails not only maximizing financial returns but also fostering economic development in host communities. This may involve creating employment opportunities, supporting local businesses and investing in infrastructure and education. Initiatives such as local procurement policies and skills development programs empower communities to participate more actively in the economic benefits generated by the copper industry, thereby promoting inclusive growth and resilience.

Traceability refers to the ability to track the journey of copper from its source to its final destination, ensuring transparency and accountability at every stage. In an industry characterized by complex global supply chains, traceability plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing environmental and social risks, as well as ensuring product authenticity and compliance with regulations. Key components of traceability in the copper supply chain include:
Responsible Sourcing: Traceability initiatives aim to verify the origin of copper and assess adherence to environmental and social standards. This involves mapping the supply chain, conducting due diligence on suppliers and implementing certification schemes such as the Copper Mark and Responsible Minerals Initiative. Collaborative platforms, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI), facilitate the exchange of best practices and promote transparency across the industry.

Chain-of-Custody Systems: Establishing robust chain-of-custody systems enables the tracking of copper throughout its journey, from extraction and processing to manufacturing and distribution. Digital technologies, such as blockchain and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), offer innovative solutions for enhancing traceability and transparency. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of transactions, authentication of product origins and verification of compliance with sustainability standards, thereby reducing the risk of fraud and unethical practices in the supply chain. Working with a trusted partner on these solutions is critical, to ensure safe handling of your sensitive data. Partnering with companies like Myneral Labs, will guarantee your safe blockchain implementation within your supply chain.
Collaborative Partnerships: Achieving comprehensive traceability requires collaboration among industry stakeholders, including mining companies, smelters, manufacturers and regulatory bodies. By sharing information and best practices, these partnerships facilitate the development of standardized traceability protocols and data-sharing mechanisms. Multi-stakeholder initiatives, such as the Responsible Copper Initiative and the Copper Mark Assurance Framework, provide platforms for collaboration and collective action towards improving traceability and sustainability in the copper industry.
Photo by Shubham Dhage / Unsplash
While the copper industry has made strides in advancing sustainability and traceability, several challenges persist:
Supply Chain Complexity: The global nature of the copper supply chain, coupled with the involvement of multiple actors across diverse geographies, poses challenges in achieving end-to-end traceability. Fragmented supply chains, inconsistent data standards and limited visibility into upstream activities hinder efforts to trace the origin of copper and assess associated risks.
Data Management: Effectively managing vast amounts of data related to copper production, including geological information, operational metrics, and supply chain transactions, requires robust systems and infrastructure. Data interoperability, data privacy concerns and cybersecurity threats present additional challenges in the implementation of traceability systems and the exchange of information among stakeholders.

Regulatory Compliance: Meeting evolving regulatory requirements, such as conflict mineral regulations and carbon emissions standards, necessitates ongoing monitoring and adaptation of practices. Regulatory uncertainty, jurisdictional differences and compliance costs can create barriers to implementing traceability initiatives and achieving alignment with international standards.
Despite these challenges, the copper industry also presents opportunities for innovation and collaboration:
Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced analytics, offer new avenues for enhancing sustainability and traceability in copper production. Machine learning algorithms can optimize resource utilization and energy efficiency, while IoT sensors can provide real-time data on environmental performance and worker safety. Integration of digital twins and predictive modeling enables proactive risk management and decision-making across the value chain.
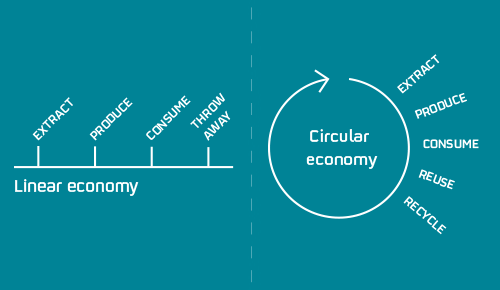
Circular Economy Practices: Embracing principles of the circular economy, such as recycling and resource recovery, can reduce the reliance on virgin copper and minimize waste generation. Closed-loop systems for copper recycling, coupled with innovations in metallurgical processes and material recovery technologies, offer opportunities to increase resource efficiency and reduce environmental impacts. Collaboration among stakeholders along the recycling value chain, including recyclers, manufacturers and consumers, is essential for scaling up circular economy initiatives and promoting the circularity of copper materials.
Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with a diverse range of stakeholders, including local communities, environmental organizations, and investors, fosters dialogue and mutual understanding, driving collective action towards sustainable outcomes. Transparent communication, participatory decision-making and stakeholder consultation processes build trust and social license to operate, enhancing the industry's reputation and resilience in the face of evolving societal expectations. Platforms for multi-stakeholder dialogue, such as sustainability roundtables and industry associations, facilitate knowledge sharing, capacity building and collaboration on shared sustainability goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fostering sustainability and traceability in the copper industry is imperative for addressing environmental and social challenges while ensuring long-term resilience and competitiveness. By embracing sustainable practices, enhancing traceability throughout the supply chain and leveraging technological innovations, the industry can pave the way towards responsible resource management and a more sustainable future. Collaborative efforts among industry stakeholders, supported by robust regulatory frameworks and innovative solutions, will be essential in realizing this vision. With a shared commitment to sustainability and traceability, the copper industry can play a leading role in driving positive social and environmental impacts, contributing to the transition towards a more sustainable and inclusive global economy.

