Critical Raw Materials - Aiding legislation through software solutions
The EU Commission's new strategy aims to secure a sustainable supply of Critical Raw Materials (CRMs), essential for green transition and economic competitiveness.
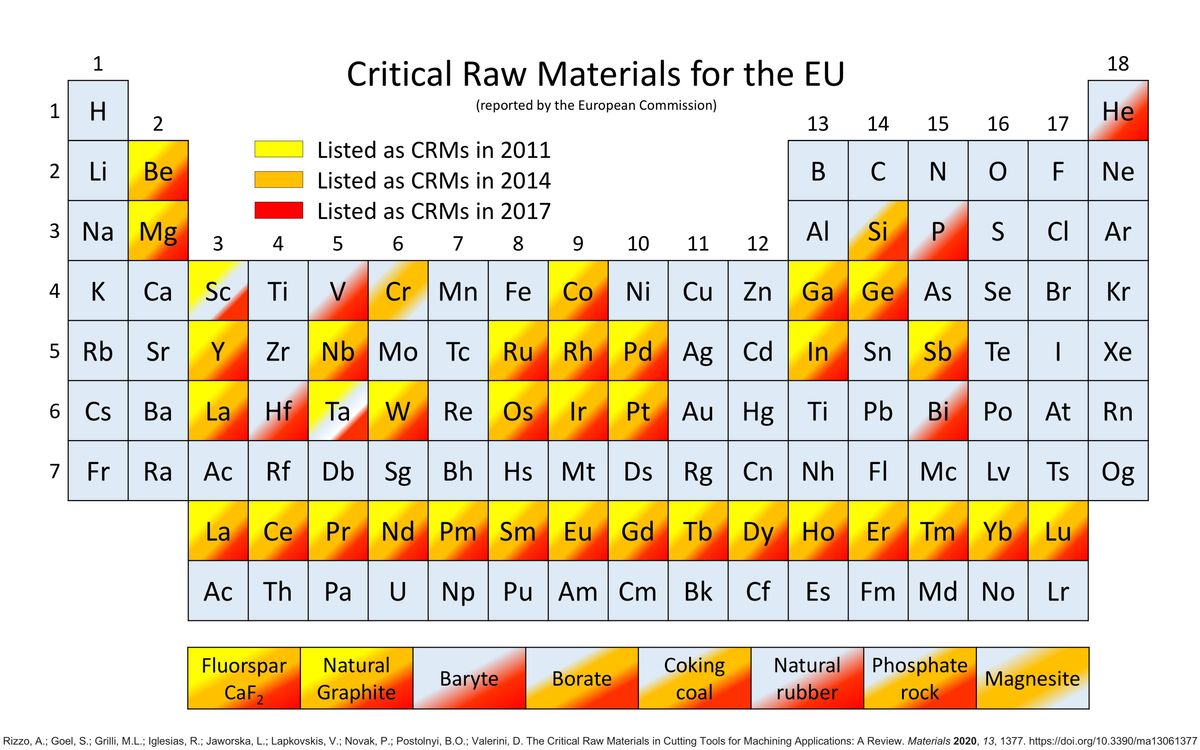
The European Commission has put forth a comprehensive strategy to ensure the European Union's access to a secure, diversified, affordable, and sustainable supply of critical raw materials. These materials are essential for several strategic sectors like aerospace, defence, net zero and digital industries. Given the increasing demand for these materials and the EU's heavy reliance on imports, this move aims to bolster the EU's economic resilience, particularly in light of challenges like the Covid-19 pandemic and energy crises such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
This act focuses on improving the EU's capacity to monitor and mitigate risks of disruptions, emphasizing the importance of circularity and sustainability.
President Ursula von der Leyen stressed the significance of refining, processing, and recycling critical raw materials within Europe, which are fundamental for technologies vital to the EU's green and digital transitions.
Understanding the difference between strategical and critical raw materials

The EU has consistently and historically sought to strengthen its economic resilience, technological advancement, and sustainable growth. One key dimension of this ambition revolves around the secure and sustainable supply of raw materials. Strategic raw materials and critical raw materials (CRMs) play a pivotal role in the EU's industrial competitiveness and innovation capabilities.
Strategic Raw Materials: These are primary materials that hold significant importance to the economic and security interests of a nation or group of nations. Their importance may be due to a variety of factors including their role in industrial production, technological applications, or defense.
Critical Raw Materials: In the EU context, CRMs are materials for which there are significant risks associated with their supply and which are also of high economic importance. This dual concern arises from a combination of factors like limited global reserves, concentration of production in a few countries, and their essential role in high-tech industries and green technologies.

The EU's industrial base, innovation capacity, and transition to a greener economy heavily rely on the unhindered access to raw materials. Here’s why CRMs are vital:
Technological Prowess: Many CRMs are essential for manufacturing cutting-edge products such as smartphones, electric vehicles, renewable energy installations, and advanced aerospace applications.
Green Transition: The EU’s ambition to transition to a more sustainable and green economy depends on CRMs. For instance, technologies for renewable energy, energy efficiency, and e-mobility require specific raw materials that are often categorized as critical.

Economic Competitiveness: With globalization and the rise of new economic giants, ensuring a steady supply of these materials is paramount for the EU’s economic competitiveness.
The impact of the new regulations
The comprehensive new strategy builds upon various reports and studies, emphasizing the significance of critical raw materials for Europe's strategic objectives, including the EU's climate and energy goals.
One key take-away from the new comprehensive strategy set forth by the EU Commission, is the need to focus on recycling energy, to preserve the precious natural resources we have - both within the EU and globally. We need to make sure that our technological advances, do not come at the price of destroying the world we live in.
The EU has long emphasized the need to develop a more circular economy where products and materials are recycled and reused to reduce dependency on external supplies. This has previously included proposals for better product design to make recycling easier and more efficient.
Due to the nature of the Critical Raw Material industry, where the global supply of Critical Raw materials are extracted and refined in a handful of countries, means that the controlling majority of refineries is structured in a quasi-monopolistic model, where the EU remains highly focused on avoiding supply chain slowdowns and single supplier dependency situations, as we saw during the COVID-19 and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Prior to these two defining events, Europe was operating under the philosophy, that active trade would avoid violent conflicts – along with the expectation that global supply chains, which have been established and refined over decades, would only ever improve – not shut down from one day to the next. These events have been eyeopeners to the EU, as it has to the rest of the world.
These new regulations try to limit the dependency on a single country supply the EU’s on-going Critical Raw Materials industries, which are so important to several high-profile industries in our world today.
Through the new strategy the EU must aim to limit their imports from a single country to maximum 65% of the EU’s annual consumption by the year 2030. Diversifying and strengthening the supply chain is considered paramount by the EU Commission.
This new benchmark comes with two strict requirements for extracted material and recycled material, which can be used in the annual EU consumption. 15% of the annual consumption must come from recycled critical and strategical raw materials, which has been much lower in the industry up until now.
This points towards an increased emphasis on recycling capabilities.
Internal steps
There's a major focus on the environment, ensuring that the secure and affordable supply of raw materials goes hand in hand with sustainability, including the rights of workers and environmental protection.
Some products must meet specific circularity requirements, including details on recyclability and the content recycled. This goes for the magnetic industry, where recycling number must be increased dramatically, to minimize the impact on your global environment.
EU Member States are mandated to implement measures for enhanced collection of waste rich in critical raw materials and facilitate its recycling.
Explorations are expected for the potential recovery of mining waste materials, not just from current mining activities, but also historical sites.
While the EU acknowledges the necessity of imports, the strategy focuses on diversifying these imports to reduce reliance on a single or few sources. In addition to this the EU recognises the importance of investing in the global partnerships, ensuring sustainable approaches throughout the global ecosystem. Acknowledging that investments in third world partners, will benefit the quality of product imported by the EU, while at the same time helping to reduce the reliance of large single country suppliers.
Could software be a solution?
Sustainability and traceability software can play a pivotal role in the critical raw materials industry. Blockchain based traceability software provides transparency throughout the supply chain. For industries dealing with critical raw materials, understanding the provenance of the materials ensures they're sourced sustainably and ethically.
By tracking the origin and journey of raw materials, companies can identify potential risks related to sourcing, geopolitical tensions, environmental impact, or other threats that might disrupt the supply chain.
Having a supply chain system, which can show you in-depth accurate live data, as well as historically accurate data, which allows you to determine exactly where a given it was throughout its journey from raw material through to finished good, means that you can unequivocally determine ownership, carbon footprint as well GPS locations for each enhancing step of the manufacturing process – through multiple involved parties.

Sharing the product data through digital product passports or white labelled platforms, will allow the end consumers full insights into the processes behind each product, and will help businesses to stay one step ahead of the competition, as the world moves towards consumer demands for a more sustainable production process. This will build brand loyalty with your downstream partners and end-users, and ultimately benefit the corporate bottom line, while making a stand for a more sustainable world.
Governments and international bodies continue to impose stricter regulations on the sourcing and utilization of raw materials, particularly those deemed "critical" or essential to the economy or defense. Blockchain based traceability software helps businesses maintain compliance through proven chain of custody abilities with these regulations by providing real-time data and reports.
Blockchain based sustainability software can provide analytics related to the environmental impact of various sourcing decisions. This can guide businesses to make more eco-friendly choices, reduce their carbon footprint, and potentially save costs.
By ensuring that your business is operating a supply chain system, which provides real-time data and analytics from actual sustainability and traceability metrics, this software can help industry leaders make more informed decisions. Whether it's about sourcing a new supplier, exploring alternative materials, or predicting future market trends, the data can guide strategy and direction.
In conclusion, sustainability and traceability software are not just tools for operational efficiency but are becoming necessities in the global landscape. For the critical raw materials industry, these tools ensure a sustainable future while addressing immediate challenges related to supply chain management, regulatory compliance, and consumer demands.
