Circular Economy Strategies: Redefining Waste as a Resource
Dive into the transformative power of the circular economy! Discover innovative strategies for sustainability across industries, with insights on waste management, product design, and blockchain technology. Join the conversation!

In recent years, the concept of the circular economy has gained significant traction as a promising approach to achieving sustainability goals across industries. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a "take-make-dispose" model, the circular economy seeks to minimize waste generation and maximize resource efficiency by redefining waste as a valuable resource. This article explores the principles of the circular economy and innovative strategies for implementing circularity in various sectors. Additionally, it examines the role of blockchain technology in enhancing transparency and accountability within circular supply chains.
The essence of the circular economy lies in its foundational principles, which advocate for the elimination of waste and pollution, the prolonged utilization of products and materials and the restoration of natural systems. This shift from a linear "take-make-dispose" model to a circular approach requires a fundamental redesign of the entire product lifecycle. It entails not only rethinking how products are designed and manufactured but also how they are utilized and ultimately disposed of. By embracing strategies centered around product longevity, reuse, repair, remanufacturing and recycling, businesses can effectively mitigate the environmental footprint of their operations while simultaneously unlocking economic value through resource optimization and innovation.
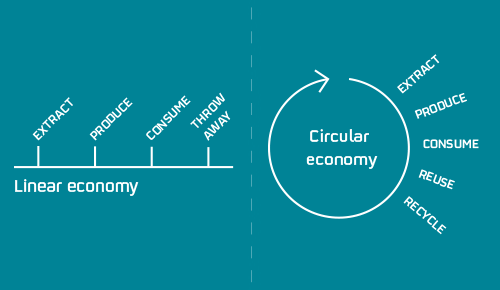
Central to the concept of the circular economy is the notion of creating regenerative systems that mimic the resilience and efficiency of natural ecosystems. By keeping materials and resources in circulation for as long as possible, companies can minimize the depletion of finite resources and reduce the burden on ecosystems. Moreover, the adoption of circular principles fosters a shift towards a more sustainable and inclusive economic model, wherein waste becomes a valuable resource and innovation thrives in the pursuit of resource efficiency. Ultimately, the transition to a circular economy represents a transformative journey towards a more resilient, equitable and environmentally sustainable future.
Innovative Approaches to Waste Management
Within the framework of the circular economy, efficient waste management stands as a foundational pillar, challenging the conventional notion of waste as an inevitable byproduct of production. Instead, companies are embracing innovative approaches that transform waste streams into valuable resources, thus closing the loop on material flows. For instance, the conversion of food waste into compost or bioenergy through anaerobic digestion not only mitigates environmental impact but also presents opportunities for generating additional revenue streams. Similarly, industrial by-products can be repurposed into raw materials for other industries, fostering a symbiotic relationship between sectors and minimizing the reliance on finite resources.

By adopting closed-loop systems and fostering collaboration across the value chain, businesses can unlock the full potential of waste as a resource. Beyond mere waste reduction, these initiatives have the power to drive economic growth, enhance resource efficiency and mitigate environmental degradation. Furthermore, by embracing circular approaches to waste management, companies can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and investors alike. Ultimately, the adoption of innovative waste management strategies not only aligns with the principles of the circular economy but also paves the way for a more resilient and sustainable future.
Product Design for Circularity
In the context of the circular economy, product design emerges as a pivotal lever for fostering sustainability and resource efficiency. Central to this approach is the concept of designing products with circularity at the forefront, integrating principles of durability, reparability and recyclability throughout their entire lifecycle. Embracing renewable materials and adopting minimalist packaging practices are just the beginning; companies must also prioritize designing products for disassembly, ensuring that components can be easily separated and recycled or repurposed at the end of their useful life. Moreover, the integration of modular design principles and standardized components not only simplifies repair and maintenance processes but also facilitates the remanufacturing of products, thereby prolonging their lifespan and reducing the demand for virgin resources.

By adopting a holistic approach to product design within the framework of the circular economy, businesses can unlock a lot of benefits beyond environmental sustainability. Enhanced durability and reparability not only extend the lifespan of products but also contribute to reduced waste generation and lower lifecycle costs for consumers. Furthermore, by embracing circular design principles, companies can foster innovation, differentiation and competitive advantage in the marketplace. Ultimately, the integration of circularity into product design not only aligns with broader sustainability objectives but also positions companies as leaders in the transition towards a more regenerative and resource-efficient economy.
Resource Recovery and Upcycling
In the essence of a circular economy, resource recovery emerges as a critical mechanism for closing the loop and circumventing the wasteful pathways that lead to landfill or incineration. Innovations such as advanced recycling, chemical recycling and upcycling hold the promise of extracting value from end-of-life products and waste streams, repurposing them into high-value secondary materials or products. Through strategic investments in infrastructure and innovation for resource recovery, businesses can not only fortify the sustainability of their supply chains but also diminish their dependence on finite resources, thus fostering resilience in the face of resource scarcity and environmental challenges.

By embracing resource recovery and upcycling within the framework of a circular economy, businesses can unlock significant economic and environmental benefits. Not only do these practices mitigate the environmental impact of waste disposal, but they also present opportunities for cost savings, revenue generation and market differentiation. Furthermore, by promoting the circularity of materials and resources, companies can bolster their reputation as responsible stewards of the environment while contributing to the broader transition towards a regenerative and sustainable economy.
Blockchain Technology for Transparency and Accountability
As companies pivot towards circular business models, the need for transparency and accountability within their supply chains intensifies. Blockchain technology stands out as a potent solution, providing a decentralized and immutable platform that meticulously tracks and traces materials throughout their journey from source to final destination. Its fundamental architecture ensures that transactions and data exchanges are securely recorded in a transparent and tamper-proof manner, thus significantly enhancing visibility into the intricate movements of materials within these supply chains. This heightened transparency not only facilitates compliance with sustainability standards and certifications but also fosters greater trust among stakeholders, enabling them to verify the authenticity and integrity of each step in the process.
Furthermore, blockchain's integration with smart contracts amplifies its utility within sustainable supply chain management. These self-executing contracts, encoded with predefined rules and conditions, have the capability to automate verification processes seamlessly. For instance, they can verify if suppliers meet specified sustainability criteria before executing transactions. By harnessing the power of blockchain-based smart contracts, companies can streamline operations, mitigate risks and foster a culture of sustainability throughout their supply chains. Ultimately, this combination of blockchain technology and smart contracts not only bolsters transparency and accountability but also serves as a catalyst for driving sustainable practices and fostering collaborative relationships among suppliers and partners.
Conclusion:
The transition to a circular economy presents immense opportunities for businesses to drive sustainability, innovation and economic growth. By embracing principles such as waste reduction, product longevity and resource recovery, companies can minimize environmental impact while unlocking new value streams. Additionally, blockchain technology holds promise as a tool for enhancing transparency and accountability within circular supply chains, ultimately advancing the goals of sustainability and responsible stewardship of resources. As we continue to navigate the challenges of a finite planet, embracing the circular economy becomes imperative for building a more resilient and sustainable future.
